5 Tips For Increasing Concentration While Reading And Learning
Efficient reading and learning require high concentration, meaning you should be fully focused on the task at hand. Here are some tips to help you increase your concentration skills.
Increasing Learning Intensity
For learning success, the following formula applies:
Learning Intensity * Learning Time = Learning Success
To make more efficient use of your learning time and achieve higher learning success with the same time investment, you need to increase your learning intensity. One approach is to shorten the duration of each learning session while increasing the focus and intensity of each. The longer you study without a break, the harder it becomes to maintain focus. Additionally, it’s helpful to set a specific goal before each session to achieve within the allotted time. For instance, you might aim to understand and explain a concept, create a mind map, read a certain number of pages, or complete specific exercises.
Finding the Right Place to Read
To read or study with focus, choose a quiet place where you won’t be disturbed and can avoid distractions. Have only the items you need for reading or studying in your immediate surroundings, so nothing distracts you. At the same time, make sure you have everything you need within reach, so you don’t have to interrupt your focus to grab, say, a highlighter. Ideally, use a specific spot almost exclusively for reading. This might be a particular armchair or a dedicated place in the garden. This way, your brain will quickly associate this spot with focused, distraction-free reading.

Meditation to Train Concentration
Meditation is an effective method for improving concentration. When meditating, focus on one thought over an extended period or try to clear your mind of all thoughts. Practicing this daily for around ten minutes helps train your brain to focus on a single task while ignoring distracting thoughts. If you develop thoughts or ideas about other tasks during a crucial activity, jot them down quickly, then redirect your focus back to the current task.
Leveraging the Serial Position Effect
The serial position effect refers to the tendency to remember information from the beginning and end of a learning session best. The primacy effect means the start is well remembered, while the recency effect implies that the end is especially memorable. In the middle of a session, memory retention often drops, so you’re more likely to remember information if it’s particularly interesting or unique.
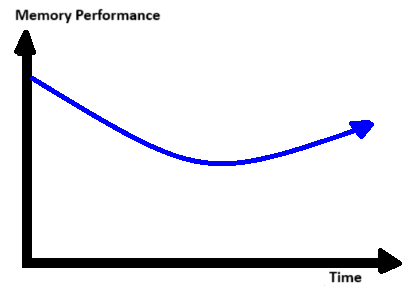
Therefore, completing a high number of short study sessions is more effective than a smaller number of long sessions. The Pomodoro Technique is an excellent approach to achieve this. With this technique, you study intensely for 25 minutes, take a five-minute break, and then repeat the cycle as many times as needed. Studying this way for four 25-minute sessions with five-minute breaks between allows you to utilize the primacy and recency effects four times. In contrast, a two-hour study session without breaks uses the serial position effect only once.
It is also helpful to review the material from each study session before taking a break. Try to recall as much as possible and give yourself a brief summary of the material. You could also create a small mind map to organize and check what you may have forgotten. This process uses the recency effect to reinforce all critical information, particularly the material learned in the middle of the session, which is otherwise more easily forgotten. You can also take advantage of the primacy effect by quickly reviewing the previous session’s material at the beginning of the new one. This is especially effective after a longer break between sessions.
Achieving the Flow State
Psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi describes “flow” as a mental state of complete immersion and engagement in an activity, an optimal state for reading and learning. In flow, you become fully absorbed in the activity, losing track of both time and self-awareness. This self-forgetfulness and time distortion help you focus completely on the task, enhancing and accelerating your learning.

Certain conditions can help you reach the flow state. It’s essential to enjoy the activity and have a clear goal in mind. You should have a specific understanding of what you want to achieve through the activity, and it’s helpful to receive immediate and continuous feedback. For example, while practicing a mathematical concept, you can check each answer to see if it’s correct.
The most important factor in experiencing flow is a balance between your skill level and the challenge presented. If the challenge is too difficult and exceeds your abilities, you may feel frustrated and stressed. Conversely, if the challenge is too easy, it can lead to boredom. Flow occurs only when the task matches your skill level well enough to be achievable but also requires you to push your limits. This way, you’re neither overwhelmed nor under-stimulated.
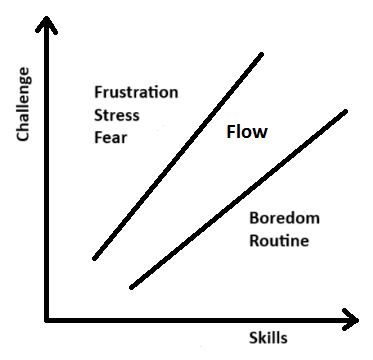
With this learning approach, you avoid wasting time on material you’ve already mastered. Instead, you step out of your comfort zone and focus on learning things that are new to you but still close enough to your current skill level.
When you reach a flow state during reading or studying, you should try to maintain it as long as possible, avoiding unnecessary breaks despite earlier guidelines. Reaching a flow state generally takes more time and boosts your concentration, creativity, and retention to a greater extent than the serial position effect. Therefore, it’s beneficial to adjust the length of your study sessions flexibly based on the nature of the task and your mental state.